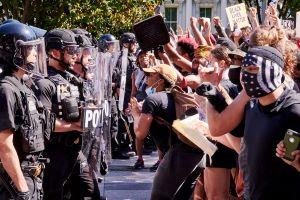As always, there was a lot going on in the realm of domestic drug policy, and here are ten of the year's most important stories.
With 2021 now receding in the rear view mirror, we look back at the good, the bad, and the ugly in the arena of drug policy around the world.
It's still pretty quiet on the medical marijuana front, but legislatures are getting back in session, so look for more action in coming weeks and months.
A former Oregon narcotics officer gets in trouble for trying to profit off black market marijuana, and a trio of prison guards go down for delivering goodies to the inmates.
An Iowa Republican legislative leader shoots down Democrats' plan for a constitutional amendment to legalize marijuana, it's the time of year for presidential pardons and commutations, and more.
You can now buy two ounces of weed at a time in Oregon instead of only one, New Hampshire lawmakers will try to override the governor's veto of a medical marijuana bill, and more.
It's January, and state legislatures are gearing up to deal with marijuana, a New York state inspector general's report unearths serious problems with prison drug testing, and more.
Wyoming marijuana legalization activists are forced to turn their aim to 2024, a New Mexico bill to legalize fentanyl test strips is coming, and more.
It's January and marijuana legalization efforts are winding up, Manhattan's new DA will refuse to prosecute some drug crimes, and more.
Kansas Democrats propose constitutional amendments to legalize medical and recreational marijuana, an Indiana lawmaker files a medical marijuana bill, and more.
A Kentucky GOP lawmaker is trying once again to get a medical marijuana bill passed, a pair of Florida lawmakers file identical bills to legalize fentanyl test strips, and more.
The nation's top spook announces an easing of rules around past marijuana use and national security clearances, the New Jersey legislature approves needle exchange expansion and syringe decriminalization bills, and more.
Whew! Another year to put in the rear view mirror, but not before we reflect on the year that was. It was a year of tragic overdose death numbers and groundbreaking responses; it was a year of advances on marijuana reform in the states but statemate in Congress; it was a year of psychedelic advance in the states and cities -- but not enough political will to reform policing, at least not federally.
As always, there was a lot going on in the realm of domestic drug policy, and here are ten of the year's most important stories. Check back next week for our Top Ten International Drug Policy Stories of 2021.

Drug-Overdose-280x212_31.jpg
The nation either neared or surpassed the one millionth drug overdose death since 1999 in 2021. Driven largely by two factors -- pandemic-related isolation and lack of access to treatment services, and the increasing presence of the highly potent opioid fentanyl in the unregulated drug supply -- overdose deaths hit an all-time high in the year ending in March 2021, with 96,779 overdose deaths reported.
That's an increase of nearly 30 percent over the previous 12-month period, according to a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report in October. And as if that were not bad enough, CDC reported in November provisional estimates that drug overdose deaths had topped 100,300 in the period from May 2020 to April 2021 -- the highest one-year overdose death toll ever.
As for that million overall dead figure, the CDC reported that through 2019 the toll had reached 841,000. We are now two years past that, and while that figure hasn't been officially recorded, just adding up the numbers makes it likely that we have already reached that horrific benchmark.
2. Nation's First Official Safe Injection Site Opens in New York City
The legality of safe injection sites -- where drug users can consume their substances in a clean, well-lit place under medical supervision -- remains unsettled under federal law, but officials in New York City decided they couldn't wait. In November, Mayor Bill de Blasio, who began calling for them in 2018, and the city Health Department announced that "the first publicly recognized Overdose Prevention Center [safe injection site] services in the nation have commenced."
The move was quickly lauded by editorials in leading newspapers such as the Los Angeles Times and the Washington Post, and by Christmas Eve, the city reported that 59 overdoses had already been reversed amid 2,000 visits to the facilities. Meanwhile, a safe injection site in Philadelphia whose opening was blocked in January by a federal appeals court after the Trump administration Justice Department moved against it, is awaiting a March filing by the Biden administration to see if it will take a more positive position allowing the facility to open.
Bills to allow safe injection sites were introduced in a number of states, including California, Massachusetts, New Mexico, Rhode Island, and Utah, although only the Rhode Island bill passed and was signed into law. Still, the opening of the New York City facilities is a historic harm reduction first for the United States, and a likely harbinger of more to come.
3. Marijuana Reform Progress in the StatesNearly half the population now lives in legal marijuana states after five states this year joined the 13 others that had previously done so, mostly at the ballot box. But the states that legalized it this year all did so via the legislative process. Those are Connecticut (Senate Bill 1201), New Jersey (Assembly Bill 21/Senate Bill 21 and Assembly Bill 897), New Mexico (House Bill 2), New York (Senate Bill S854A), and Virginia (House Bill 2312/Senate Bill 1406).
This movement comes as marijuana legalization continues to garner strong public support, with a November Gallup poll reporting "a new high" of 68 per cent report. There was other marijuana-friendly legislative action in the states as well: Louisiana decriminalized it, four states (Colorado, Delaware, New Mexico, Virginia) passed expungement laws, Alabama approved medical marijuana (although not in smokeable form), and 17 states approved medical marijuana expansion laws. Weed is on a roll.
4. Democrats Haven't Got Federal Marijuana Legalization Done, and It's Not Looking So Great for Next Year, Either
With Democrats in control of Congress after the November 2020 elections, hopes were high that this could be the year federal marijuana prohibition would be ended. The House had already passed a legalization bill at the end of the last Congress, Senate Majority Leader Charles Schumer (D-NY) was pushing for it, and even if President Biden opposed full legalization and would only go as far as supporting decriminalization, that was a bridge that could be crossed when we came to it.
Now, at the end of 2021, that bridge is still a ways down the road. The Marijuana Opportunity, Reinvestment and Expungement (MORE) Act (HR 3617), sponsored by House Judiciary Committee Chair Rep. Jerrold Nadler (D-NY), passed the House of Representatives a year ago. But that was a different Congress, meaning it has to pass the House again. In this Congress it's only passed the Judiciary Committee, in late September, and hasn't moved since. On the Senate side, Schumer and Sens. Cory Booker (D-NJ) and Ron Wyden (D-OR) rolled out an initial draft of their legalization bill, the Cannabis Administration and Opportunity Act in mid-July, but have yet to formally file legislation.
One big reason for the impasse is that Democrats are at odds among themselves, tussling over whether to hold out for full legalization replete with social equity measures, or to go for incremental measures in the meanwhile, such as banking access for state-legal cannabusinesses through the SAFE Banking Act (HR 1996). That bill passed the House and was inserted into the annual defense funding bill, only to be removed at the insistence of Senate leadership in the former camp, including Majority Leader Charles Schumer (D-NY).
The fight over how to approach marijuana reform federally has split not only the Democrats, but also the drug reform movement, with groups like the Drug Policy Alliance calling for not passing banking except as part of a full legalization bill, while NORML and the Marijuana Policy Project lobbied hard for the SAFE Act.
As the year came to an end, Reps. Earl Blumenauer (D-OR) and Barbara Lee (D-CA) told the Congressional Cannabis Caucus that Congress would take up marijuana reform in the spring. But with an election year looming, Congress evenly divided, and not even all Democratic senators sure votes on marijuana legalization, Congress looks more likely to be nibbling at the edges of federal pot prohibition rather than ending it -- or perhaps to do nothing. There are dozens of marijuana-related bills filed, from expungement to veterans' access to easing research barriers and more. In 2021, nibbling at the edges may be the best we can do.
Meanwhile, in November, a GOP legislator, Sourth Carolina Rep. Nancy Mace filed her own bill, the States Reform Act, which would legalize marijuana at the federal level. It would do so by removing marijuana from Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act, leaving it up to the states to set their own marijuana policies. The bill would also set a three percent federal excise tax, and release and expunge the records of those convicted of federal marijuana offenses. Mace said her bill represented a compromise that could gain support from both Republicans and Democrats.
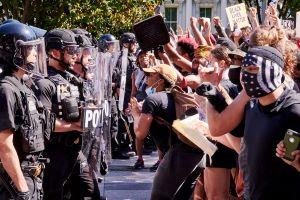
Last year's mass mobilization around George Floyd's death has yet to translate to new laws restraining police misbehavior. (CC)
Following the death of George Floyd while being arrested by Minneapolis police and the massive mobilizations it generated, the impetus grew to reexamine and reform police practices. The spirit of reform in response to the crisis took root in both houses and both parties, with Republican South Carolina Senator Tim Scott filing a tepid Just and Unifying Solutions to Invigorate Communities Everywhere (JUSTICE) Act last year. But that bill lacked key provisions demanded by Democrats, such as an end to qualified immunity for police officers in civil lawsuits, and it died at the end of the last session.
That spirit of reform was embodied in February, when the House passed the George Floyd Justice in Policing Act (HR 1280), sponsored by Rep. Karen Bass (D-CA). That bill would make it easier to convict a police officer for misconduct in a federal prosecution and limit qualified immunity as a defense against liability in a private civil action against an officer. It also restricts the use of no-knock warrants, chokeholds, and carotid holds and creates a National Police Misconduct Registry, among other provisions.
Senator Cory Booker (D-NJ) envisioned something similar in the Senate when in June he announced his framework for comprehensive police reform legislation. Like the House bill, it too reformed qualified immunity so that people could actually recover damages from police who violate their constitutional rights. It too would make it easier to federally prosecute police misconduct. And it too would create a National Police Misconduct Registry, as well as banning racial profiling and providing incentives for states to adopt policies banning no-knock warrants, chokeholds, and other airway-restrictive holds in their use-of-force policies.
Booker and Scott would become the point men in a month's long effort to craft a police reform bill with bipartisan support over the course of the summer. But by September, the negotiations had hit a dead end, with Booker telling reporters: "We weren't making progress -- any more meaningful progress on establishing really substantive reform to America's policing," he said. And with that, federal police reform was dead for the year.
One of the irresolvable issues was qualified immunity, on which Scott and the Republicans refused to budge. Instead, in a statement noting the end of negotiations, Scott claimed "Democrats said no because they could not let go of their push to defund our law enforcement" and then, with a complete unawareness of irony, complained about using "a partisan approach to score political points."
So far in the Congress, it has been justice delayed. Will it end up being justice denied? There is still a year left in the session, so stay tuned.
6. The Biden Administration's Partial Embrace of Harm Reduction
From the outset, the Biden administration is proving to be the friendliest ever toward harm reduction, even though it has yet to acknowledge one of the most effective harm reduction interventions: safe injection sites (or "supervised consumption sites" or "overdose prevention centers"). The first signal came in March, when the administration included nearly $4 billion for substance abuse disorder and mental health, including funding for harm reduction activities such as needle exchange services in the coronavirus relief bill. The bill allocated $30 million in community-based funding for local substance use disorder services like syringe services programs and other harm reduction interventions.
Then, on April 1, the administration gave us the first big hint of what its drug policy will look like as it released the congressionally-mandated Statement of Drug Policy Priorities for Year One. That document contains a heavy dose of drug prevention, treatment, and recovery, but also prioritizes "enhancing evidence-based harm reduction efforts." The same month, it allowed federal funds to be used to buy rapid fentanyl test strips.
After a quiet summer, Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Xavier Becerra made news in October when he announced the department's overdose prevention strategy and committed to more federal support for harm reduction measures, such as needle exchanges, increased access to naloxone, and test strips to check drugs for the presence of fentanyl. He even suggested the agency might be open to safe injection sites, but in a sign of the delicacy of the subject in this administration, HHS quickly walked back the comments: "HHS does not have a position on supervised consumption sites," the statement read. "The issue is a matter of ongoing litigation. The Secretary was simply stressing that HHS supports various forms of harm reduction for people who use drugs."
In November, the administration released model naloxone legislation. The administration on Wednesday released model legislation to help states improve access to naloxone treatment for opioid overdoses. The model bill encourages people to obtain naloxone, protects them from prosecution when administering it, requires health insurance to cover it, and provides increased access to it in schools and correctional facilities.
Also in November, that $30 million from the coronavirus relief bill got real when SAMHSA announced it had launched $30 million harm reduction grant funding opportunity to "help increase access to a range of community harm reduction services and support harm reduction service providers as they work to help prevent overdose deaths and reduce health risks often associated with drug use."
The Biden administration is clearly moving in the direction of harm reduction, but where it comes down on safe injection sites is still muddy. The Justice Department is preparing a brief in the case of Safehouse, a proposed Philadelphia safe injection site that was blocked from opening after the Trump administration Justice Department persuaded the 3rd US Circuit Court of appeals that it violated the Controlled Substance Act's "crack house" provision. That brief will be a key indicator of whether the administration is prepared to fully embrace harm reduction, but we are going to have to wait until next year to find out.
7. Oregon Leads the Way on Drug Decriminalization, Others Are Vying to Follow
With the November 2020 passage of Measure 110 with 59 percent of the vote, Oregon became the first state to decriminalize drug possession, and by year's end, the initial results were looking pretty good. Because the measure tapped into marijuana tax revenues to fund treatment and harm reduction services, those programs are getting a hefty $302 million in much needed funding over the next two years.
While the numbers are not in yet for this first year of decriminalization, there were roughly 9,000 drug arrests a year prior to passage of Measure 110, and thousands of Oregonians who would have been arrested for drug possession this year have instead faced only their choice of a $100 fine or a health assessment. It won't be 9,000 fewer drug arrests, though, because some felony drug possession arrests (possession of more than the specified personal use amounts) have been downgraded to still arrestable misdemeanors. Still, it will be thousands fewer people subjected to the tender mercies of the criminal justice system and all the negative consequences that brings.
In the wake of the Oregon vote, a number of other states saw decriminalization bills introduced -- Florida, Kansas, Maine, New York, Vermont, Virginia and Washington -- and so did Congress, when Representatives Bonnie Watson Coleman (D-NJ) and Cori Bush (D-MO in June filed the Drug Policy Reform Act (DPRA), whose most striking provision is drug decrim. DPRA is the first time decriminalization bill to be introduced in Congress.
Also on the decrim front this year, efforts are underway in Washington, DC and Washington state to put initiatives on the ballot next year. The public seems to be ready: A summer poll from Data for Progress and The Lab found that 71 percent of respondents said federal anti-drug policies aren't working and reform is needed and 59 percent supported decriminalizing drug possession. A slightly earlier ACLU/Drug Policy Alliance poll around the same time had even stronger results, with 83% saying the war on drugs had failed and 66% supporting decrim. Decriminalization is starting to look like an idea whose time has come.
8. Conservative State Supreme Courts Negate the Will of the Voters
The November 2020 elections resulted in a clean sweep for drug reform initiatives, with marijuana legalization being approved in four states and medical marijuana in two states. But in two cases, marijuana legalization in South Dakota and medical marijuana in Mississippi, Republican-dominated state Supreme Courts moved to effectively negate the will of the voters.
In South Dakota, Constitutional Amendment A won with 54 percent of the vote, but acting at the behest of South Dakota anti-marijuana Republican Governor Kristi Noem, a county sheriff and the head of the Highway Patrol sued to block the measure. They won in circuit court and won again when the state Supreme Court threw out Amendment A, ruling it unconstitutional because it violated a provision limiting constitutional amendments to one subject. Noem's victory may prove ephemeral, though: The activists behind Amendment A are already collecting signatures for a 2022 initiative, and the state legislature didn't even wait for the Supreme Court decision to decide it is ready to legalize marijuana in the next session.
In Mississippi, Initiative 65 won with 74 percent of the vote, but a Republican local official successfully challenged it, and in May, the Republican-dominated state Supreme Court threw it out -- managing to wipe out the state's initiative process as it did so. Under the state constitution, initiative campaigns are required to get one-fifth of signatures from each of five congressional districts, which seems straightforward enough. The only problem is that since congressional reapportionment after the 2000 census, the state only has four districts, making it impossible for any initiative to comply with the constitutional language.
The state has seen numerous initiatives since 2000, with none of them challenged. When faced with the conundrum, the Supreme Court could have found that constitutional language "unworkable and inoperable on its face," but instead pronounced itself bound to find Amendment 65 "insufficient" because it cannot meet the five-district requirement.
The legislature has been working to craft a medical marijuana bill, but Republican Governor Tate Reeves is not happy with the legislative language and has refused to call a special session on medical marijuana. Mississippians will have to wait for 2022.
9. House Votes to End Crack/Powder Cocaine Sentencing Disparity, But Senate Dallies
In September, in an effort to undo one the gravest examples of racially-biased drug war injustice, the House voted to end the federal sentencing disparity between crack and powder cocaine. HR 1693, the Eliminating a Quantifiably Unjust Application of the Law (EQUAL) Act of 2021, passed on a vote of 361-66, demonstrating bipartisan support, although all 66 "no" votes came from Republicans. Amidst racially-tinged and "tough on drugs" political posturing around crack use in the early 1980s, accompanied by significant media distortions and oversimplifications, Congress passed the Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1986, cosponsored by then-Senator Joe Biden (D-DE) and signed into law by Ronald Reagan. Under that bill, people caught with as little as five grams of crack faced a five-year mandatory minimum sentence, while people would have to be caught with 500 grams of powder cocaine to garner the same sentence.
While race neutral on its face, the law was disproportionately wielded as a weapon against African-Americans. Although similarly small percentages of both Blacks and Whites used crack, and there were more White crack users than Black ones, Blacks were seven times more likely to be imprisoned for crack offenses than Whites between 1991 and 2016. Between 1991 and 1995, in the depths of the drug war, Blacks were 13 times more likely to be caught up in the criminal justice meat grinder over crack. And even last year, the US Sentencing Commission reported that Black people made up 77 percent of federal crack prosecutions.
After years of effort by an increasingly broad alliance of drug reform, racial justice, human rights, religious and civic groups, passage of the 2010 Fair Sentencing Act took a partial step toward reducing those disparities. The FSA increased the threshold quantity of crack cocaine that would trigger certain mandatory minimums -- instead of 100 times as much powder cocaine than crack cocaine needed, it changed to 18 times as much.
The 2018 FIRST STEP Act signed by President Trump allowed people convicted before the 2010 law was passed to seek resentencing. And now, finally, an end to the disparity is in sight. The Senate version of the bill is S. 79, introduced by Senator Cory Booker (D-NJ) and cosponsored by fellow Democrat Dick Durbin (IL) and GOP Senators Rand Paul (KY), Rob Portman (OH), and Thomas Tillis (NC). After the vote, they prodded their Senate fellows to get moving. But the Senate bill has yet to move after being filed 11 months ago.
10. Psychedelic Reform Movement Broadens in States and Cities
The movement to ease or undo laws criminalizing psychedelic substances continued to broaden and deepen in 2021. Detroit and Seattle joined Denver and Oakland in the ranks of major cities that have embraced psychedelic reform, with the Seattle city council approving a psychedelic decrim measure in October and Detroit voters approving a psychedelic decrim measure in November.
A number of smaller towns and cities went down the same path this year too, including Cambridge, Massachusetts in February, Grand Rapids, Michigan, in September (joining Ann Arbor), Easthampton, Massachusetts in October (joining Cambridge, Northampton, and Somerville), and Port Townsend, Washington, in December.
Psychedelic reform bills are now making their way to statehouses around the country, with bills showing up in eight states by March and a handful more by year's end. Most of them have died or are languishing in committee, and a much-watched California psychedelic decriminalization bill, Senate Bill 519, has been pushed to next year after passing the state Senate only to run into obstacles in the Assembly. Two of them passed, though: New Jersey S3256, which lessens the penalty for the possession of any amount of psilocybin from a third degree misdemeanor to a disorderly persons offense punishable by up to six months in jail and/or a $1,000 fine, became law in February. Then Texas House Bill 1802, which would expand research on therapeutic psychedelics, became law in June.
Meanwhile, building on Denver's pioneering psilocybin decriminalization in 2019, a national advocacy group, New Approach PAC, has filed therapeutic psychedelic and full psilocbyin legalization initiatives aimed at 2022. Oakland activists have announced a "Go Local" initiative under which people could legally purchase entheogenic substances from community-based local producers. The move aims to build on the city's current psychedelic decriminalization ordinance, passed in 2019.
back to top
With 2021 now receding in the rear view mirror, we look back at the good, the bad, and the ugly in the arena of drug policy around the world.
1. The International Criminal Court Eyes Philippines Drug War Killings

Protestors denounce Duterte's bloody drug war. (hrw.org)
Rodrigo Duterte's term as Filipino president may be coming to an end, but his bloody legacy of drug war murders is going to haunt him. For us, last year actually begins in December 2020, when the International Criminal Court (ICC) announced its
preliminary examination of the Filipino drug war showed evidence of crimes against humanity, clearing the path toward a formal investigation into what are estimated to be more than 30,000 killings. At that point, the ICC had to determine whether the Philippine justice system has is responding to the killings in a legitimate way. If the Philippines couldn't or wouldn't hold perpetrators accountable, the court could take the case.
ICC attention was only one piece of the mounting international pressure over the Duterte killings. For example, in February, US Senators Edward J. Markey (D-MA), top Democrat on the East Asia and Pacific Subcommittee, Dick Durbin (D-IL), and Patrick Leahy (D-VT) called for the full exoneration and release of Philippines drug war critic Senator Leila De Lima, who had then been detained on bogus, politically-motivated charges for four years. Now, it's been nearly five years, and she is still behind bars.
In May, a blustering Duterte vowed he would not open up police records about the killings and warned drug dealers that: "If I am there, I will really kill you. I don't care if there's TV around. I will really kill you."
In June, the ICC Office of the Prosecutor concluded its preliminary investigation and announced there was sufficient evidence to request authorization to proceed with an official investigation, which prompted the Duterte administration to say it would not cooperate with the ICC investigation.
In August, Duterte again resorted to bluster, this time taunting the ICC during his last State of the Nation address and daring the court to record his threats against those who would "destroy" the country, saying: "I never denied -- and the ICC can record it -- those who destroy my country, I will kill you. And those who destroy the young people of my country, I will kill you, because I love my country."
But while Duterte blustered, his Justice Department was attempting to blunt the ICC investigation by announcing it had finished a review of 52 drug war killing cases. It was a weak effort though: The cases represented only a tiny fraction of the more than 6,000 killings for which the Philippines National Police took responsibility. And it wasn't enough to stop the ICC, which announced in September that it would open an official investigation into the killings, setting the stage for summonses and possible arrests warrants if requested by Prosecutor Karim Khan.
In October, once again moving to blunt the investigation, the Justice Department announced that 154 police could be liable for drug war misconduct and then announced it would review thousands of drug war killings. The government also invoked a provision of the ICC's Rome Treaty to suspend the investigation while its request to defer it got considered. The following month, the ICC temporarily did suspend its official investigation, as per the treaty. "The prosecution has temporarily suspended its investigative activities while it assesses the scope and effect of the deferral request," ICC chief prosecutor Karim Khan wrote.
The year ended with human rights groups urging the ICC to get back to investigating Duterte: "We ask the ICC not to allow itself to be swayed by the claims now being made by the Duterte administration," said the National Union of People's Lawyers, which represents some victims' families. The national justice system is "extremely slow and unavailing to the majority of poor and unrepresented victims", the statement said. The Duterte government's claim that existing legal mechanisms could bring justice to Duterte's victims was "absurd," said Human Rights Watch. "Let's hope the ICC sees through the ruse that it is," said Brad Adam, HRW Asia director.
2. Afghanistan's Government Falls, Opium Remains
Afghanistan has been the world's largest producer of opium since the 1990s, except for one year when the Taliban banned it the first time they held power. Opium never went away during the nearly two-decade long occupation by the US and NATO forces, and despite Taliban declarations to the contrary, it does not look like the trade is going anywhere.
When the Taliban completed their conquest of the country by seizing Kabul in August, Taliban spokesman Zabihullah Mujahid vowed that their new government would not let Afghanistan become a full-fledged narco-state: "We are assuring our countrymen and women and the international community that we will not have any narcotics produced," Mujahid said. "From now on, nobody's going to get involved (in the heroin trade), nobody can be involved in drug smuggling."
By October, the price of opium was rising in local markets, having tripled since the Taliban took power as buyers anticipated an opium shortage because of the possible ban, but the ban has yet to materialize.
And a UN Office on Drugs and Crime report that same month made it clear why the ban is unlikely to materialize. In a country now in economic crisis because the foreign spending that propped up the previous regime has vanished, UNODC reported that the spring opium crop had generated between $1.8 and $2.7 billion for the Afghan economy, also noting that "much larger sums are accrued along illicit drug supply chains outside Afghanistan."
The 2021 crop was some 6,800 tons, up 8% over 2020. Given the devastation of the Afghan economy and the unlikelihood that the Taliban will move against a crop that supports hundreds of thousands of Afghan families, it's entirely possible that the crop next spring will be even larger. As one farmer told the UNODC, "There is no work, all the families are in debt, and everyone's hope is opium."
3, Mexican Drug War Violence Just Keeps Going
Sixteen years after then-President Felipe Calderon called out the military to combat rising violence, Mexico's drug prohibition-related violence continued unabated in 2021, with more than 25,000 killed by the end of November.
Amidst the quotidian violence, some notable incidents stand out: in March, an attack on a police convoy in Mexico state left 13 officers dead; in May, presumed cartel gunmen ambushed Joel Ernesto Soto, director of the Sinaloa State Police, on Monday, killing him on the outskirts of Culiacan, the state capital; in June, gunmen in SUVs representing warring factions of the Gulf Cartel ranged across the border town of Reynosa, just across the Rio Grande River from McAllen, Texas, leaving a toll of at least 14 and as many as 18 dead; in August, masked men claiming to represent the Jalisco New Generation Cartel released a video where they threaten to kill Milenio TV anchor Azucena Uresti over what they called "unfair" coverage. And on and on.
The west central state of Michoacan was particularly plagued by cartel violence in 2021, beginning with an April massacre by the Jalisco New Generation Cartel (CJNG) of rival gang members in the municipality of Aguililla. In May, warring cartels blocked highways and burned vehiclesin Aguililla and neighboring municipalities.
As violent clashes and blockades continued through the year, residents of those municipalities took to the streets in September took to the streets in Septemberto excoriate the military for staying in its barracks and demand military intervention to fight the cartels. It didn't work. That same month, the Jalisco New Generation Cartel beheaded five men manning a checkpoint on the edge of Tepalcatepec designed to keep the drug gangs out. And in November, the Jalisco New Generation Cartel struck again, killing five men and six boys near the town of Tarecuato in the north of the state near the border with the state of Jalisco as it pursued its war with local criminal gangs.
When it comes to US-Mexico cooperation in the war on drugs, 2021 was not a good year. It began with a huge diplomatic spat around the DEA's arrest in late 2020 of former Defense Minister Salvador Cienfuegos, who was subsequently released after loud protests from Mexico, with Mexican President Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador, who personally accusing the DEA of making up the case against Cienfuegos. The US retorted with the Justice Department sharply rebuking Mexico for releasing a massive trove of evidence in the aborted drug trafficking case against Cienfuegos. Mexico then countered with a call for a DEA internal probe of the "fabricated" case.
Amidst the controversy, US investigations into the cartels were paralyzed as a law enacted in December requiring US officials to report their law enforcement contacts in the country to Mexican officials, whom they view as largely corrupt, went into effect. In May, US and Mexican officials told Reuters the fight against Mexican drug trafficker had "ground to a halt"because of strained relations between the two counties.
But in October, there was a glimmer of hope for fans of continued anti-drug coordination between the two countries. Leading Biden administration officials including Secretary of State Anthony Blinken, Homeland Security Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas, and Attorney General Merrick Garland met with their Mexican counterparts to try to create a new framework for cooperation on drugs, crime, and border issues. The high-profile meeting came after months of quiet talks to rebuild relations.
4. Mexico Didn't Get Marijuana Legalization Done (Again)Two years after the Mexican Supreme Court found marijuana prohibition unconstitutional and ordered the government to legalize it, the Senate finally passed a legalization bill in late 2020. The measure appeared to have momentum on its side, especially after the Chamber of Deputies approved it in March. Under the bill, people 18 and up would be able to possess up to an ounce of marijuana and grow up to six plants (although one controversial change in the Chamber of Deputies would require home growers to register with the state). The bill also created a system of taxed and regulated legal marijuana commerce.
The momentum appeared to hold through April, when the bill won two Senate committee votes in as many days but then hit a last-minute snag when it ran into opposition from unhappy with the revised version of the bill. With that, the bill was dead in the water until the congress returned to work in September.
Progress remained slow when lawmakers returned. It was only in November that a draft legalization bill was being circulated among senators, and while there were hints that a vote could happen in December, it didn't. Maybe in 2022.
5. Bangladesh Drug War Killings Draw Pushback
In May, Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina approved an anti-drugs campaign aimed at methamphetamines, and by mid-month police had killed 86 people and arrested 7,000. About the killings, police claimed they were only defending themselves in confrontations with drug traffickers, but family members and activists claimed they were executions. The opposition Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) also said the anti-drug campaign was part of an effort to target and intimidate it.
By the end of May, the toll had risen to 115, with more signs of extrajudicial killings and complaints from the BNP that some party workers had been killed during the campaign despite no connection to the drug trade. Authorities continued to claim that dead dealers had died in crossfire or in gunfights with police, but more families complained that their relatives had been arrested and then killed in custody. Most of the raids were carried out by the RAB (Rapid Action Battalion), a controversial force that human rights groups have repeatedly accused of abuses, including forced disappearances and extrajudicial killings.
By June, the United Nations was responding, with UN High Commissioner for Human Rights Zeid Ra'ad Al Hussein saying the extrajudicial killings of suspected drug dealers must be "immediately halted" and the perpetrators brought to justice. "Every person has the right to life and they do not lose their human rights because they sell drugs," he added. At that time, the toll stood at 130 dead and 13,000 arrested.
After that, the campaign quieted down, but there is no sign of any Bangladeshi investigations into the killings and human rights abuses in in the late spring. The United States, however, was paying attention, and in December, imposed sanctions on the RAB for human rights abuses, abductions, and hundreds of extrajudicial killings going back to 2018, targeting not only drug dealers, but also opposition party members, journalists, and human rights activists.
6. Pushing the Boundaries in Canada
Canadian cities, provinces, and activists pressed the Liberal federal government on drug reform issues throughout the year, with important struggles being waged around drug decriminalization and the vanguard issue of a safe drug supply, as well as a noteworthy milestone reached in opioid maintenance therapy.
The Liberals started the year off by introducing a sweeping criminal justice reform billthat would make arrests for drug possession only one option for police, end all mandatory minimum sentences for drug offenses, end some other mandatory minimums, and open the way for conditional (probationary) sentences for a variety of offenses. But critics who demanded deeper reforms scoffed that it was too little, too late.
In April, British Columbia showed what deeper reforms might look like when it formally requested permission from the federal government for provincial drug decriminalization. That same month, saying the Liberal's reform bill didn't go far enough, the New Democratic Party's health critic, MP Don Davies filed a federal drug decriminalization bill.

VANDU is the vanguard.
The city of Vancouver
also sought an exemption from federal drug laws to enact decriminalization.The city recommended the decriminalization of one gram or 10 rocks for crack cocaine, 1.5 grams for amphetamines, two grams for opioids such as heroin and fentanyl, and three grams for cocaine. That did not sit well with the city's vanguard drug user activists, who
harshly criticized the possession limits. At that point, the Vancouver Area Network of Drug Users (VANDU) announced that it is withdrawing from talks with the city, and it and other drug policy advocates complained that drug users were largely excluded from the decriminalization process and that police have too large a role.
The push for decriminalization continued throughout the year. In October, nearly 70 organizations across the country, including the HIV Legal Network, the British Columbia Civil Liberties Association, and the National Association of Women and the Law, urged Prime Minister Trudeau to decriminalize drug possession. And in November, Toronto moved toward decriminalizationas the city's top health officer, Dr. Eilenn de Villa, recommended that the board of health approve a request to the federal government to exempt city residents from criminal charges for small-time drug possession.
But even though decriminalization is in the Liberals' platform, the party under Justin Trudeau is not ready to go there yet. After calling elections in August, necessitating a restart on January criminal justice reform bill, and despite the rising clamor for decriminalization, the Liberal government refiled the bill anyway.
In the summer, an even more direct challenge to drug prohibition was underway as British Columbia moved toward providing a "safe supply" of illicit drugs to street users.A provincial policy directive in British Columbia requires all local health authorities to develop programs to provide pharmaceutical quality opioids and stimulants to street drug users in a bid to reduce overdose deaths.
A Vancouver elected official and local activists got in on the action, too, when Councilwoman Jean Swanson and a pair of drug user advocacy groups, Drug User Liberation Front (DULF) and the Vancouver Area Network of Drug Users (VANDU) handed out free cocaine, heroin, and methamphetamine to drug users in the Downtown Eastside in a bid to dramatize the need for a safe drug supply. They also wanted to "raise awareness of the deeply flawed aspects of the Vancouver Model of decriminalization, including disproportionate influence of the Vancouver Police Department, unreasonably low drug thresholds, and lack of provisions for safe supply."
The following month, they were at it again, handing out a "safe supply" of drugs to mark International Overdose Awareness Dayto show the "life-saving potential of a community-led response to the crisis of prohibition in Canada" as an alternative to Vancouver's proposed model of decriminalization. And in September, DULF and VANDU formally asked the federal government to allow buyers' clubs for hard drugs. They requested a formal exemption from federal criminal drug laws so that no one is prosecuted for operating a "compassion club" to distribute those drugs.
And in October, the province of Alberta expressed interest in a safe drug supply. The prairie province's United Conservative government proposed that a committee of Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs) look into the pluses and minuses of offering pharmaceutical versions of opioids and other addictive substances to people dependent on them.
Meanwhile, magic mushroom shops were sprouting in Vancouver. A handful of shops selling magic mushrooms and other psychedelic substances are operating in in the city even though selling magic mushrooms remains illegal in Canada. One such shop, the Coca Leaf Café & Mushroom Dispensary on East Hastings Street, is owned by long-time drug activist Dana Larsen. "We're sitting in a place that is unique in the world. There's nowhere else where you can get the same range of substances and things that we do right here," Larsen said.
And last but not least, in September, a Vancouver clinic began providing take-home prescription heroin,a North American first. The program began as an emergency response to the COVID epidemic, when the provincial health authority allowed clinic staff to deliver syringes filled with heroin to patients so they could stay isolated for 10 to 14 days, but now the patients can take it home themselves.
7. Malta Becomes First European Union County to Legalize Marijuana -- Germany, Luxembourg Next?
The Maltese parliament approved a bill legalizing marijuanaon December 14, and President George Vella signed it into law four days later, making the country the first member state of the European Union to do so. The law allows citizens 18 and over to possess up to seven grams of marijuana and cultivate up to four plants at home, harvesting up to 50 grams from them. The law does not envision commercial sales but allows nonprofit cooperatives to produce marijuana to be sold to members, with an upper limit on membership per coop of 500.
Either Germany or Luxembourg could be next. In October, the government of Luxembourg unveiled its marijuana legalization proposal, which would allow people 18 and over to grow up to four plants and possess up to three grams in public. Like Malta, the Luxembourg law does not envision commercial sales, but people would be allowed to buy and trade marijuana seeds for their home gardens. The proposal still has to be approved by parliament.
And in November, the three parties who have formed Germany's new governing coalition -- the Social Democrats, the Greens, and the Free Democrats -- agreed to legalize marijuana and its sale. The coalition is prepared to "introduce the regulated sale of cannabis to adults for consumption purposes in licensed stores," according to the coalition's health group's findings paper. It is not clear, however, whether home cultivation will be allowed.
8. Italy's Pending Referendum on Marijuana and Plant Psychedelics
Italy is on the cusp of a bold drug reform move. A number of pro-reform activist groups and political parties including the Radicals launched a ballot campaignin for a referendum to legalize the cultivation of marijuana and other psychoactive plants and fungi, such as psilocybin mushrooms. They faced several challenges: First, they had to obtain half a million valid voter signatures by month's end and have the signatures validated by the Supreme Court of Cassation, then the Constitutional Court would have to rule that the measure is in line with the constitution, and only then, President Sergio Mattarella would set the date for the referendum, which would ask whether that portion of the country's drug law criminalizing the cultivation of marijuana and psychoactive plants should be stricken.
In October, activists met their first challenge, turning in some 630,000 raw signatures. They were able to meet their signature-gathering goals so quickly because a pandemic-related policy change allowed them to collect signatures online instead of only in person.
Now, after having staved off an attempt by rightist parties to block it, the fate of the referendum is before the courts. If it wins final approval from the Constitutional Court, which will determine whether it conflicts with the constitution, international treaties, or the country's fiscal system, voters could go to the polls on the issue sometime between April 15 and June 15.

There's tons of cocaine around these days. (Pixabay)
In June, the White House Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP -- the drug czar's office) released its annual estimate of coca cultivation and potential cocaine production in Bolivia, Colombia, and Peru, the three perennial coca and cocaine producing nations. What is at first glance most striking in the current report is that for the first time, one nation -- Colombia -- produced more than 1,000 metric tons of cocaine.
But a closer reading of the report, which details coca cultivation and cocaine production going back to 2010, produces an even more striking finding: Over the decade that the report covers, the total amount of potential cocaine production in the three countries has more than doubled, from 914 tons in 2010 to a whopping 2,132 tons in 2020. In other words, Colombia alone produced more cocaine in 2020 than the whole region did a decade earlier.
The UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) does its own annual estimates of global potential cocaine production, and while they differ from those of the United Status, they outline the same massive expansion of cocaine. According to UNODC numbers compiled at Statista, beginning in 2004, 1,000 tons or more (slightly more in most years) was produced every year except 2012, 2013, and 2014, when it dipped down into the 900s. That series, which ended in 2019, has cocaine production topping out at 1,976 tons in 2017.
In the most recent edition of the UNODC's World Drug Report, that organization also reported that cocaine production had doubled, but put the period of doubling from 2014 to 2019, when it registered 1,784 tons.
Take your pick of the numbers. Either way, there is a lot more cocaine being produced these days than just a decade ago, tons more of it.
10. World Health Organization Declines Move Toward Labeling Kratom a Controlled Substance
The World Health Organization's (WHO) Expert Committee on Drug Dependence (ECDD) recommended in November that kratom not be subjected to a "critical review," which could have been a first step toward labeling it a controlled substance subject to international and national controls. The ECDD did a "pre-review" of kratom at its October meeting and found there was inadequate evidence to recommend a critical review.
WHO had begun the "pre-review" based in part on a "country-level report indicating the potential for abuse, dependence and harm to public health from" the chemical compounds in kratom. But it found concerns about fatalities associated with kratom to be overstated: "Kratom can produce serious toxicity in people who use high doses, but the number of cases is probably low as a proportion of the total number of people who use kratom," WHO stated in the document. "Although mitragynine [the active alkaloid in kratom] has been analytically confirmed in a number of deaths, almost all involve use of other substances, so the degree to which kratom use has been a contributory factor to fatalities is unclear."
back to top
It's still pretty quiet on the medical marijuana front, but legislatures are getting back in session, so look for more action in coming weeks and months.
MississippiMississippi Legislature Convenes, Is Set to Take Up Medical Marijuana. The legislature is back in session, and medical marijuana is on the front burner. Voters approved medical marijuana at the polls in November 2020 only to have the results nullified by the state Supreme Court, and lawmakers have vowed to enact the will of the voters by passing a medical marijuana bill. It was supposed to have been done in a special session late last year, but Gov. Tate Reeves (R) never called it because he was unsatisfied with the proposed legislation. Now, the legislature will give it another try.
New Hampshire
New Hampshire Lawmakers to Take Up Vetoed Medical Marijuana Bill. Legislators will try this week to override Gov. Chris Sununu's veto of a bill that would have allowed nonprofit medical marijuana treatment centers to organize as for-profit businesses. In his veto message, Sununu said he vetoed the bill because it would create monopolies that could dominate the marketplace if and when recreational marijuana is legalized. The bill passed the Senate with a veto-proof majority, but passed the House on a voice vote, leaving it unclear whether there is a veto-proof majority there.
back to top
A former Oregon narcotics officer gets in trouble for trying to profit off black market marijuana, and a trio of prison guards go down for delivering goodies to the inmates. Let's get to it:
In Jackson, Michigan,
a state prison guard was arrested December 20 after police found evidence he was smuggling drugs into the Parnall Correctional Facility. Correctional Officer Thomas Saverio Daugherty, 46, went down after the department contacted internal investigators with information he was involved in contraband and then executed a search warrant at his home. He is charged with furnishing contraband to a prisoner and is looking at up to five years behind bars.
In Klamath Falls, Oregon, a former Klamath County narcotics detective and current reserve officer was arrested December 23 was arrested in connection with an illegal marijuana grow. Peter Michael Shephard, 63, leased part of his rural property to a man who claimed to be growing hemp but who never sought a hemp permit and who was actually growing unpermitted marijuana. But police said Shephard never sought confirmation his partner had a hemp permit. He and his partner are both charged with unlawful manufacture of marijuana and engaging in a financial transaction in property derived from unlawful activity.
In Oklahoma City, an Oklahoma County Jail detention officer was arrested last Tuesday for allegedly smuggling drugs into the facility. Officer Reagan Widener, 27, went down during an employee search county's Special Investigative Unit when investigators found an authorized cell phone and then searched her vehicle, finding 4.5 grams of marijuana, a loaded handgun and a digital scale, authorities said. Widener admitted to previously receiving $2,000 for bringing in tobacco and packages of unknown drugs to an inmate. She is charged with distribution of controlled substance, possession with intent to distribute, use of a firearm while committing a felony, and carrying a weapon, drugs or alcohol into jail, according to the release. Widener, who had worked at the jail since August, has since been fired.
In Atlanta, a federal prison guard was arrested last Thursday for allegedly being involved in a scheme to smuggle drugs and other contraband into the US Penitentiary Atlanta. Guard Patrick Shackleford and two inmates have been arraigned on federal bribery, smuggling, and drug charges for the scheme, which went on between approximately June 2018 and February 2019. Shackleford was also a plumbing supervisor and conspired with inmates on his plumbing crew to bring contraband in via a visitors' bathroom.
back to top
An Iowa Republican legislative leader shoots down Democrats' plan for a constitutional amendment to legalize marijuana, it's the time of year for presidential pardons and commutations, and more.

New York city safe injection sites have already reversed 59 overdoses. (Creative Commons)
Iowa Republican Leader Shoots Down Democrats' Plan for Marijuana Constitutional Amendment. Yesterday, we noted a call by a trio of Iowa Democratic state senators for a constitutional amendment to legalize marijuana. It didn't take long for a key Republican to shoot it down. Senate Judiciary Committee Chairman Sen. Brad Zaun of Urbandale said he had no intention of bringing the proposal for a vote and derided marijuana legalization as a "gimmick." Republicans control both the governor's office and the legislature.
Harm Reduction
New York City Safe Injection Sites Are Already Saving Lives. The NYC Health Department announced Tuesday that the nation's first sanctioned safe injection site has already been heavily utilized and saved dozens of lives. The department announced that 59 overdoses had been reversed at the sites, which have seen more than 2,000 visits from people seeking a safe, secure place to shoot up.
These initial results are "promising" and demonstrate how the sites "reduce needless suffering and avoidable deaths," said Health Commissioner Dave Chokshi. "The simple truth is that Overdose Prevention Centers save lives -- the lives of our neighbors, family and loved ones."
A day earlier, the New York City Board of Health unanimously approved a resolution that touts evidence supporting the efficacy of a harm reduction approach to drug use and endorses the city's move to authorize safe consumption sites. The resolution urges "the federal government and New York State provide authorization of such overdose prevention centers and continue to expand funding and support for harm reduction services and medications for opioid use disorder treatment."
The Trump administration moved to block a safe injection site from opening in Philadelphia. It is not yet clear what the position of the Biden administration will be, but advocates are waiting for a Justice Department response in the pending Philadelphia case for a hint of what is to come. The Philadelphia safe injection site, Safehouse, is waiting for the DOJ to submit its position to an appeals court, but in what advocates see as a positive sign, the date for DOJ to do that has been pushed back from November 5 to March 7, 2022.
Sentencing
White House Says Biden Has "Every Intention" of Commuting Sentences for Some Drug Prisoners. White House Press Secretary Jen Psaki said Tuesday that President Biden has "every intention of using his clemency power" this year but was non-specific about when that might happen. When asked at a press briefing if there were any plans for commutations, Psaki said: "I don't have anything to preview at this time. I would just reiterate that the president has every intention of using his clemency power," she said. "And there has been some reporting which is accurate out there about looking at nonviolent drug offenders, but I don't have anything to update you on at this point in time."
back to top
You can now buy two ounces of weed at a time in Oregon instead of only one, New Hampshire lawmakers will try to override the governor's veto of a medical marijuana bill, and more.

Moving to Montana soon? Now you can buy pot there -- if you're in the right county. (Gmark1/Creative Commons)
Montana Legal Marijuana Sales Begin. On New Year's Day, the state became the latest to allow legal recreational marijuana sales. The move comes more than a year after voters approved a pair of complementary marijuana legalization initiatives in November 2020 with 57 percent of the vote. But it's not on sale everywhere in the state: Under the law, counties where majorities voted for legalization can have pot shops, but in counties where majorities voted against the initiative cannot allow the shops unless the matter is approved in a county-wide vote.
Oregon Doubles the Amount of Marijuana People Can Buy. On December 28, the Oregon Liquor and Cannabis Commission approved new rules that include raising the amount of marijuana that people can purchase on a single occasion from one ounce to two ounces. That went into effect on New Year's Day. The state will now also allow home delivery of marijuana across city and county lines.
Medical Marijuana
New Hampshire Lawmakers to Take Up Vetoed Medical Marijuana Bill. Legislators will try this week to override Gov. Chris Sununu's veto of a bill that would have allowed nonprofit medical marijuana treatment centers to organize as for-profit businesses. In his veto message, Sununu said he vetoed the bill because it would create monopolies that could dominate the marketplace if and when recreational marijuana is legalized. The bill passed the Senate with a veto-proof majority, but passed the House on a voice vote, leaving it unclear whether there is a veto-proof majority there.
Ayahuasca
IRS Denies Tax Exempt Status to Iowa Ayahuasca Church. The Iowaska Church of Healing has lost its bid to win tax-exempt status with the Internal Revenue Service. The church holds a "Sacrament of Ayahuasca" where its members use the hallucinogen for spiritual and physical healing, although its leader says he has never conducted such ceremonies at his home or anywhere else in the state. The church applied for tax-exempt status in January 2019.
back to top
It's January, and state legislatures are gearing up to deal with marijuana, a New York state inspector general's report unearths serious problems with prison drug testing, and more.

Part of a 254-pound shipment of fentanyl seized at the border. (CBP)
Maryland Lawmaker Pre-Files Legislation to Place Adult-Use Marijuana Legalization on State's 2022 Ballot. Del. Luke Clippinger (D-Baltimore City), chairman of the House Cannabis Referendum and Legalization Workgroup that formed last summer to study adult-use legalization in Maryland, has pre-filed House Bill 1. If approved by three-fifths of the state House and Senate, the bill would ask voters the following referendum question: "Do you favor the legalization of adult-use cannabis in Maryland?" The bill will be formally introduced when the legislative session opens on January 12.
Ohio Marijuana Legalization Initiative Campaign Comes Up Short on Signatures, Has Only Days Left. The secretary of state's office has informed the Coalition to Regulate Marijuana Like Alcohol that it had gathered only 119,825 valid voter signatures when it needed 132,887 to get to the first stage of the "initiated statute" process. That means the Coalition now has until January 13 to come up with 13,062 more valid voter signatures. If the campaign meets that hurdle, the legislature would have four months to address the underlying marijuana legalization legislation. If the legislature fails to act or rejects it, supporters can collect another 132,887 signatures to place it on the statewide ballot, likely in November 2022. The initiative would allow people 21 and older to buy and possess up to 2.5 ounces of marijuana and grow up to six plants.
South Dakota Lawmakers Have Marijuana Legalization Bill Ready to Go. With the legislative session set to open next week, state legislative leaders are ready to advance a marijuana legalization bill, Senate Bill 3, that was drafted by a marijuana working group and approved by the legislative leadership. The bill would restore the will of the voters, who approved legalization at the ballot box in 2020 only to have it thrown out as unconstitutional by the State Supreme Court. Legalization isn't the only marijuana-related item on lawmakers' minds; of 38 pre-filed bills, 25 deal with marijuana, mostly with medical marijuana, which voters already approved last year and which the state has moved ahead on.
Drug Testing
New York State Inspector General Investigation Determines Hundreds of Incarcerated New Yorkers Denied Due Process and Endured Severe Punishment as a Result of Egregious Administrative Failure in Drug Testing Program. State Inspector General Lucy Lang announced Tuesday that incarcerated people across the state were subjected to internal penalties including solitary confinement, had their sentences lengthened, parole hearings delayed, family visitation privileges revoked, and suffered other punishments, based upon a highly flawed drug testing program between January and August 2019 administered by the New York State Department of Corrections and Community Supervision (DOCCS).
Lang's investigation found that these sanctions, which impacted more than 1,600 people during that eight-month period, were based upon preliminary positive results for the presence of the opioid buprenorphine, without obtaining confirmation by more specific alternative tests as was required by the instructions provided by the manufacturer, Microgenics Corporation. DOCCS then failed to properly investigate the reason for a significant spike in positive test results after the implementation of the new tests or take prompt corrective action upon being presented with scientific evidence that many of the results were false positives.
The investigation also found that representatives from Microgenics frustrated the efforts of the incarcerated people who attempted to challenge their charges at administrative hearings by providing false or misleading information about the tests' reliability. Changes are being made as a result of the investigation, including an end to the use of solitary confinement for failing a drug test.
Opioids
US Customs and Border Protection Seized More Fentanyl Than Heroin at the Border Last Year. In Fiscal Year 2021, which ran from October 2020 to September 2021, US Customs and Border Protection seized more at least 11,200 pounds of fentanyl at the border, more than double the 5,400 pounds of heroin seized. CBP also seized 319,447 pounds of marijuana, 97,638 pounds of cocaine, 190,861 pounds of methamphetamine, and 10,848 pounds of ketamine, for the fiscal year 2021. The seizure figures come as fentanyl is implicated in about two-thirds of the record wave of drug overdose deaths plaguing the US this year.
back to top
Wyoming marijuana legalization activists are forced to turn their aim to 2024, a New Mexico bill to legalize fentanyl test strips is coming, and more.
psilocybin molecule (Creative Commons)
Wyoming Activists to Focus on 2024 for Decriminalization, Medical Marijuana Initiatives. Having decided they cannot gather enough voter signatures in time to put marijuana decrim and medical marijuana initiatives on the 2022 ballot, reformers are turning their attention to 2024. They cited poor weather conditions, the pandemic, and slow action on their petitions by state officials for coming up short for this year. They would have needed 41,776 valid voter signatures by next month to make the 2022 ballot, and only have about 30 percent of that number at this point.
Medical Marijuana
Mississippi Legislature Convenes, Is Set to Take Up Medical Marijuana. The legislature is back in session, and medical marijuana is on the front burner. Voters approved medical marijuana at the polls in November 2020, only to have the results nullified by the state Supreme Court, and lawmakers have vowed to enact the will of the voters by passing a medical marijuana bill. It was supposed to have been done in a special session late last year, but Gov. Tate Reeves (R) never called it because he was unsatisfied with the proposed legislation. Now, the legislature will give it another try.
Psychedelics
Psilocybin Clinical Trial Confirms Safety of Group Psychedelic Sessions. A new study published in the The Journal of Psychopharmacology found no detrimental effects from administering psilocybin in a group setting. The study reported the results of a large clinical trial checking on both short- and long-term effects of administering the drug. While researchers in the 1960s studied the effects of psychedelics when administered in a group setting, since interest in medicinal applications of psychedelics rebounded in recent years, almost all research has focused on the administration of the drugs to individuals.
Harm Reduction
New Mexico Attorney General to Push Bill Legalizing Fentanyl Test Strips. Faced with a 25 percent increase in drug overdose deaths from 2019 to 2020, Attorney General Hector Balderas (D) says he is getting behind pending legislation to make fentanyl test strips legal. Under current state law, they are considered drug paraphernalia. State Rep. Tara Lujan (D-Santa Fe) says she will file the bill this week and that it also has the support of the governor and the state health department.
International
Abu Dhabi Court Sentences Two Filipinos to Death for Drug Dealing. The Abu Dhabi Criminal Court has sentenced two unnamed Filipinos to death after convicting them of possessing and selling "narcotics and psychotropic substances."
The death sentences contradict the position of the UN Office on Drugs and Crime, as in this 2019 statement: "As part of the United Nations Secretariat, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) does not support the use of the death penalty. Just last December [2018], more countries than ever before -- 121 Member States -- supported a General Assembly resolution calling for a moratorium on the use of the death penalty. The three international drug control conventions, which form the foundation of the global drug control system that has been agreed by nearly every country in the world, cannot be used to justify the use of the death penalty for drug-related offences alone. Application of the death penalty may also impede international cooperation to fight drug trafficking, as there are national laws that do not allow the exchange of information and extradition with countries which may impose capital punishment for the offences concerned. The dangers posed by illicitly-trafficked drugs are evident and lives are at stake. But use of the death penalty cannot provide durable solutions or protect people."
back to top
It's January and marijuana legalization efforts are winding up, Manhattan's new DA will refuse to prosecute some drug crimes, and more.
Marijuana PolicyIowa Lawmakers Release Proposal to Put Marijuana Legalization on the Ballot. Three state Senate Democrats have filed a constitutional amendment to legalize marijuana in the state. The proposal would put the state's Alcoholic Beverage Commission in charge of regulations, would allow people 21 and over to possess and purchase marijuana, and set up a system of taxed and regulated production and sales. To become law, the amendment would have to be approved by two General Assemblies and then put on the next election ballot. Senators Joe Bolkcom (D-Iowa City), Sarah Trone Garriott (D-Windsor Heights), and Janet Petersen (D-Des Moines) introduced the proposal.
New Hampshire House Refuses to Pass or Kill Marijuana Legalization Bill. The House on Tuesday voted down an attempt to kill a marijuana legalization bill, House Bill 237, but then also refused to pass it. The bill would have legalized recreational marijuana use for adults 21 years old and older, regulated its use and commercial sales, and tax those sales. The motion to kill the bill failed on a 171-158 vote, while a motion to pass the bill failed on a 170-163 vote. The House then decided on a 300-32 vote to table the bill.
New York Governor Announces $200 Fund for Social Equity Marijuana Businesses. The state will create a $200 million fund to assist social equity applicants trying to get marijuana business licenses, Gov. Kathy Hochul (D) announced during her State of the State address Wednesday. But the funding mechanism -- a "public/private" model based on licensing fees and taxes -- has some minority industry members concerned that the funding will only be available after the industry has already been established, still leaving social equity applicants in an adverse position.
Oklahoma Activists File New Marijuana Legalization Initiative. Activists on Tuesday filed a new marijuana legalization initiative with state officials. This time, the local activists are being backed by the national New Approach PAC, which has backed a number of successful initiatives in other states. A different group of state activists has already filed its own legalization initiative. This newest measure would allow people 21 and over to possess up to an ounce, grow up to six plants and six seedlings, and set up a system of taxed and regulated marijuana sales. If and when the initiative is approved for signature-gathering, the campaign will have 90 days to come up with 94,911 valid voter signatures to qualify for the ballot.
Medical Marijuana
Mississippi Governor Says Proposed Current Dosage Amount for Medical Marijuana is Too High. Governor Tate Reeves (R) is digging in his heels on concerns about how much marijuana medical marijuana patients could use under proposed legislation. "If 10 percent of the Mississippi population gets a marijuana card, that's 300-thousand Mississippians," he said. "At 11 joints a day, that's 3.3 million joints a day, 100 million joints a month,1.2 billion joints on the streets of Mississippi a year and I just think that's too much to be on the streets." Voters approved medical marijuana in the November 2020 elections, only to see it thrown out by the state Supreme Court. Both Reeves and the legislature have vowed to enact medical marijuana legislation, but they have yet to reach an agreement.
Prosecution
Manhattan DA Announces Office Will Not Prosecute Certain Offenses, Including Some Drug Offenses. New Manhattan District Attorney Alvin Bragg issued a memo this week directing his prosecutors to seek jail or prison time only for the most serious offenses and not prosecute charges such as marijuana misdemeanors, fare-jumping, trespass, unlicensed vehicle operation, prostitution, or resisting arrest unless the offense is accompanied by another misdemeanor or felony. Also, small-time drug sellers will not be charged with felonies and will be eligible for diversion. Bragg is only the latest big city progressive prosecutor to embrace such an approach to prosecution; prosecutors in places like Houston, Los Angeles, Philadelphia, and San Francisco have been leading the way.
International
Duterte Says He Will "Never Apologize" for Drug War Deaths. Outgoing Philippines President Rodrigo Duterte remains unrepentant about the thousands of people killed in his bloody war on drugs. In a major speech Tuesday, he said police doing their duty had a right to fight back when their lives were endangered, and that he would not apologize for his actions. "I will never, never apologize for the deaths of those bastards," he said in English, before adding in Tagalog, "Kill me, imprison me, I will never apologize." Official government numbers put the death toll in Duterte's drug war at 6,200, but human rights groups say the real toll is more than 30,000. The Duterte administration is currently trying to fend off an International Criminal Court investigation of human rights abuses in its drug war.
back to top
Kansas Democrats propose constitutional amendments to legalize medical and recreational marijuana, an Indiana lawmaker files a medical marijuana bill, and more.

Psilocbyin mushrooms could be legalized for therapeutic purposes under a Washington state bill. (Creative Commons)
Kansas Democrats Announce Plan for Marijuana Legalization, Medical Marijuana Constitutional Amendments. House Minority Leader Tom Sawyer (D) and Assistant Minority Leader Jason Probst (D) announced on Thursday they will introduce a pair of constitutional amendments to put the issues of marijuana legalization and access to medical marijuana directly to the voters. Democratic lawmakers next door in Iowa announced a similar move earlier this week. Republican-led legislatures in both states have blocked further marijuana law reforms, but the Democrats are hoping the legislatures will at least pass the measures and let the voters decide.
New Hampshire House Again Votes to Legalize Marijuana. For the third time since 2019, the House has approved a marijuana legalization bill, this year's version being HB629-FN. The bill would allow adults to possess up to three-quarters of an ounce of marijuana and to grow up to six plants. It could be traded or given away but not sold. The House passed a broader bill that would have allowed taxed and regulated sales in 2019, only to see it die in the Senate. And a bill similar to this one passed in 2020, only to die in the Senate. Gov. Chris Sununu (R) opposes legalization, but this bill passed the House with a veto-proof majority. It now heads to the Senate.
Medical Marijuana
Indiana Lawmaker Files Medical Marijuana Bill. State Senator Greg Taylor (D-Indianapolis) has filed a bill to allow medical marijuana use in the state. The measure, Senate Bill 231, would create a medical marijuana program where patients and caregivers with a physician's recommendations could possess and use marijuana. It would also set up a regulatory authority to oversee the program. Prospects are uncertain in the Republican-dominated state legislature.
Psychedelics
Washington State Lawmakers File Therapeutic Psilocybin Bill. State Senators Jesse Salomon (D) and Liz Lovelett (D) have introduced a bill that would allow people to use psilocybin and psilocin, the psychoactive ingredients in magic mushrooms, with the assistance of a trained and state-licensed psilocybin services administrator. The bill, Senate Bill 5660, is titled the Psilocybin Wellness and Opportunity Act. People would have to go to a licensed service center to partake, unless they suffer certain medical conditions or are unable to travel, in which case they could receive psilocybin at home and meet remotely with a facilitator. Under the bill, the state Department of Health would issue licenses and regulate the new industry. The act would further establish the Washington Psilocybin Advisory Board within the department to advise on issues such as available scientific and social research, best practices for supported use as well as criteria for the bill's social opportunity program.
back to top
A Kentucky GOP lawmaker is trying once again to get a medical marijuana bill passed, a pair of Florida lawmakers file identical bills to legalize fentanyl test strips, and more.

Life is now a bit easier in the Big Easy. (CC)
Months After City Council Pardons Small-Time Marijuana Offenses, New Orleans Police Finally Quit Citing People. The New Orleans Police Department last Friday announced that when it comes to marijuana offenses, the agency will "no longer issue citations for simple possession alone." The move came only after a local media outlet published a story, "Despite council ordinance, people still forced to appear in court on simple possession of marijuana citations." The city council had unanimously approved an ordinance removing all criminal penalties for simple marijuana possession back in August, but the department kept citing people for it anyhow -- until now.
Medical Marijuana
Kentucky Republican Files Medical Marijuana Bill. State Rep. Jason Nemes (R) is renewing his efforts to get a medical marijuana bill passed. After having been rebuffed in past sessions, he is back again this year with House Bill 136, which would create a restrictive medical marijuana program that would allow neither home cultivation nor the smoking of marijuana flowers. Patients could vape whole-plant products, though. Specific rules for the program -- such as qualifying conditions -- would be set by regulators after the bill is passed, but the following conditions will be included: any type of cancer, epilepsy and seizure disorders, multiple sclerosis, nausea or vomiting and chronic, severe, intractable or debilitating pain.
Harm Reduction
Florida Lawmakers File Identical Bills to Decriminalize Fentanyl Test Strips. State Rep. Andrew Learned and state Sen. Shevrin Jones have filed identical bills to decriminalize a life-saving tool, known as fentanyl testing strips, for preventing opioid overdose.
The two bills, House Bill 6101 and Senate Bill 1668, would remove drug testing equipment from Florida's legal definition of drug paraphernalia, which currently includes "all equipment, products, and materials of any kind which are used, intended for use, or designed for use in planting, propagating, cultivating, growing, harvesting, manufacturing, compounding, converting, producing, processing, preparing, testing, analyzing, packaging, repackaging, storing, containing, concealing, transporting, injecting, ingesting, inhaling, or otherwise introducing into the human body a controlled substance."
Under current state law, possession of fentanyl test strips is a misdemeanor and distribution, even by harm reduction groups, could be charged as a felony.
New York City to Install Naloxone Vending Machines in Bid to Reduce Overdoses. City health officials last month published a Public Health Vending Machine Initiative to install ten vending machines with the opioid overdose reversal drug naloxone in them. "The purpose of this RFP is to support low-barrier access to overdose prevention and harm reduction supplies," the department said. The machines will also dispense sterile syringes and other wellness goods, such as safe sex items and toiletries.
The machines will be installed in all five boroughs of the city in neighborhoods most impacted by drug overdoses. The request for proposals has a response due date of January 20 and a contract start-up date of February 7. The program will run through June at a cost of $730,000.
back to top
The nation's top spook announces an easing of rules around past marijuana use and national security clearances, the New Jersey legislature approves needle exchange expansion and syringe decriminalization bills, and more.
psilocybin molecule (Creative Commons)
Director of National Intelligence Gives Clarification on Marijuana Issues and Clearance Holders. In guidance released late last year, Director of National Intelligence Avril Haines clarified the intelligence community's policy regarding security clearances for people who have used marijuana. Under previous policy, people needed to have not used marijuana for one to two years before applying for a national security position, but now the policy is that past marijuana use should not be determinative, but that they needed to stop using if they were being considered for a position: "In light of the long-standing federal law and policy prohibiting illegal drug use while occupying a sensitive position or holding a security clearance, agencies are encouraged to advise prospective national security workforce employees that they should refrain from any future marijuana use upon initiation of the national security vetting process, which commences once the individual signs the certification contained in the Standard Form 86 (SF-86), Questionnaire for National Security Positions."
The new guidance also addresses investing in marijuana businesses, warning that people seeking clearances should not do so, and it warns people seeking security clearances to be wary of using CBD products -- although it doesn't forbid it. "With respect to the use of CBD products, agencies should be aware that using these cannabis derivatives may be relevant to adjudications in accordance with SEAD 4." In other words, it could show up on a drug test.
Virginia Republican Files Bill to Eliminate Social Equity Funding in Marijuana Program. State Sen. Thomas Norment Jr. has filed a bill, Senate Bill 107, that would eliminate social equity funding for the state's recreational marijuana program. The bill would delete the line in last year's marijuana legalization law that channels 30 percent of revenues into a marijuana equity investment fund. Although Democrats still control the state Senate, minority business advocates worry that the bill could still pass and are calling it an effort to dismantle provisions in the law that have strong public support. If the bill does not pass, the funding will go supporting licensing opportunities for small and minority-owned marijuana businesses.
Harm Reduction
New Jersey Legislature Approves Bills Ending Requirement for Municipal Approval for Needle Exchanges. The legislature has passed the Syringe Access Bill (S-3009/A-4847) and the Syringe Decrim Bill (S-3493/A-5458), a pair of bills whose aim is to address the state's opioid overdose epidemic by easing access to clean needles, legalizing possession of needles, and expanding access to addiction services. The first pair of bills ends the requirement that municipalities pass an ordinance to okay local needle exchanges, while the second pair of bills legalized needle possession.
International
Canada Opens Legal Pathway for Access to Psychedelic Treatment with MDMA, Psilocbyin. Health Canada has amended federal regulations to allow doctors to request access to restricted drugs, such as MDMA and psilocybin, for patients undergoing psychedelic therapy. The regulatory change will allow physicians to use the Special Access Program, which allows healthcare practitioners to access drugs that have shown promise in clinical trials, or are approved in other countries, to seek permission to employ the drugs as therapeutics. The amendment to the Food and Drug Regulations was published in the Wednesday edition of the Canada Gazette, Canada's version of the federal register.
back to top